describe autoclaving process|autoclave process steps : factories However, autoclave sterilization is not limited to the medical device industry; it finds applications in various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, research laboratories, and . As an alternative to DEPC, which can inhibit enzymatic reactions if not completely removed, NEB’s nuclease-free water or readily available Milli-Q purified water is sufficiently free of RNases.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Congratulations on the purchase of your new Delta-Q Autoclave. The technical documentation provided is designed as a part of this product. Always keep this documentation handy. The .
What exactly is an autoclave, and what’s the point of one? Learn everything you need to know about autoclaves and their sterilization process here. Image 3: Vertical construction of autoclave with labelled image Types of Autoclaves There are 02 types of autoclave systems commercially available: Gravity displacement. In this . However, autoclave sterilization is not limited to the medical device industry; it finds applications in various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, research laboratories, and . Figure 3. 1. Vessel. The vessel is the main body of the autoclave and consists of an inner chamber and an outer jacket. Laboratory and hospital autoclaves are constructed with .
In conclusion, autoclave sterilization is a vital process that ensures the safety and integrity of medical instruments, laboratory equipment, and supplies. By effectively eliminating . The focus of the case study is to show a complete stage of manufacturing process starting from modeling in CAD system passing through CAM system, transferring NC code, .
The gravity displacement autoclaves are primarily used to process laboratory media, water, pharmaceutical products, regulated medical waste, and nonporous articles . Equipment Needed for the Autoclave Sterilization Process . For autoclave sterilization, a facility needs a way to contain and protect the tools undergoing sterilization. .
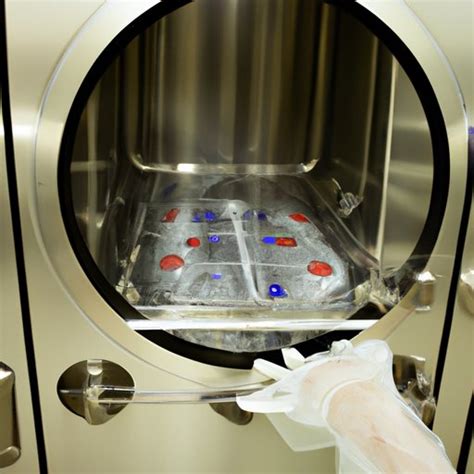

how does alcohol affect a refractometer
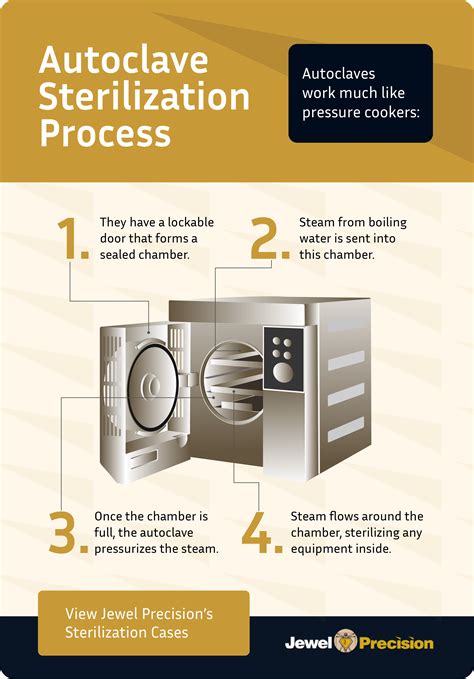
Thanks to the pressurization component of the process, an autoclave can reach steam temperatures higher than normal, which allows them to operate relatively quickly and . What is Autoclaving? Autoclaving is the most effective method of sterilizing the lab equipment specially for liquid handling products to kill harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and . The autoclaving process makes them safer for handling and transport, it does not change the disposal endpoint. When using an autoclave, the following guidelines should be . The most common temperature for autoclave sterilization is 121°C, but many autoclaves allow cycles at higher temperatures, such as 132°C and 134°C. How long does it .
Moist heat sterilization works by causing the coagulation of proteins within microbes. This process irreversibly damages the microorganisms’ cellular structures, leading . Cooling: After sterilisation, the autoclave begins a controlled cooling process. This prevents thermal shock to delicate materials and ensures safe removal of items. Venting: The . These parameters are often used to describe sterilization procedures that use high heat, such as autoclaving. Boiling is one of the oldest methods of moist-heat control of . Autoclaves require a constant supply of water to generate steam. They are equipped with water reservoirs or direct water connections, ensuring a continuous supply .
In healthcare, ensuring the sterility of medical instruments is crucial. Steam sterilization, or autoclaving, stands as a key defense against microbial contamination. Utilizing .
Autoclave or steam sterilization is a moist heat sterilizing technique that has prominent applicability in laboratories, industries, and hospitals to purify different samples, equipment and .
The temperature within the medical waste autoclave reaches high temperatures – up to 132 degrees Celsius – throughout the cleaning process. The high temperature of the steam will .%PDF-1.7 %âãÏÓ 4276 0 obj > endobj 4288 0 obj >/Encrypt 4277 0 R/Filter/FlateDecode/ID[1564B57341670E45ABF57AA58477559A>]/Index[4276 29]/Info 4275 . In healthcare, the term "autoclave" is typically used as the nomenclature to describe a Steam Sterilizer. ANSI/AAMI 4, which provide standards and guidelines for the . Autoclaves generally follows these steps: Objects or instruments (also called load materials) to be sterilized are placed in an autoclave-compatible bag and then into a .
An autoclave is the most common method of sterilization in the laboratory working on moist heat. Sterilization is the process of removing or destroying all microorganisms .
Autoclave. The basic autoclave process has been in commercial use for decades, primarily in the medical field for sterilizing instruments, some manufacturing uses, and in the sterilizing of . Decontamination is a term used to describe a process or treatment that renders a medical device, instrument, or environmental surface safe to handle. Sterilization, disinfection, . Introduction. The maintenance of aseptic conditions is an absolute necessity in a tissue culture lab. That's why you should be aware of the several sterilization techniques used .
Autoclave Sterilization Cycle or Autoclaving Process. Autoclave Sterilization Cycle : The autoclave is frequently used to sterilize various pieces of equipment and media in practical labs, .
Autoclaves are essential devices in various fields, including healthcare, laboratories, and industrial settings, where sterilization is crucial. These. . the autoclave gradually releases .
why autoclave is used
Hydrothermal synthesis reactor generally comes in a two variety; the first is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or Teflon lined hydrothermal autoclave reactors and the .
describe autoclaving process|autoclave process steps